Nexcelom’s ADCC Assay Types
ADCC Assay With Neutrophil, NK, and CIK Cells
- Perform non-toxic, non-radioactive ADCC assay
- Use different immune cells to perform ADCC assays
- Generate kinetic data for ADCC assay
- Optimize assay development by imaging the same plate over the duration of the assay
Non-Toxic Calcein AM Release ADCC Assay
As part of the adaptive immune system, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) is a critical mechanism of the immune system’s defense. Typically, the invading pathogen or a cancer cell is identified by a specific therapeutic antibody and is subsequently killed by immune cells that recognize and bind to the therapeutic antibody. Traditionally, cytotoxicity assays such as ADCC assays have been performed using various release assays described below.
| Detection Method | Description | Existing Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Radioactivity Release | Measure the release or radiolabels, 51Cr, 101In in the supernatant | Handling hazardous material; Indirect measurement of cell death |
| Fluorescence Release | Measure the release of calcein AM fluorescent molecules in the supernatant | Indirect measurement of cell death; Endpoint assay only |
| LDH Release | Measure the release of cytosolic enzyme in the supernatant | Indirect measurement of cell death; Endpoint assay only |
| Luciferase Reporter Assay | Measure luciferase as the cells die | Indirect measurement of cell death |
| Flow Cytometry | Measure the number of viable cells and viability in the sample | Cannot perform in plates; Must trypsinize for adherent cells |
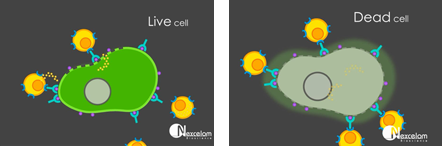
By labeling the target tumor cells with non-toxic, non-radioactive calcein AM, we can monitor the killing of the tumor cells by the immune effector cells by performing a calcein AM release assay.
Celigo image cytometer acquires whole-well images and reports the number of live calcein positive cells. By imaging the same plate over a period of time, or by plating different E:T ratios we can examine the dynamic killing process of target tumor cells visually and quantitatively.
Neutrophil-Mediated ADCC Assay using Direct Cell Counting of Calcein AM Stained Target Cells
Celigo Experimental Protocol
- Target cells (adherent or suspension) are collected and stained with calcein AM
- Target cells are seeded in the wells of microplates
- Antibodies are added to the wells at different concentrations
- Effector cells are added to the wells at different E:T ratios
- The wells are scanned and analyzed using Celigo for direct cell counting calcein AM stained target cells
- Time-course % cytotoxicity data is generated to show ADCC by reduction of target cells
Time-Dependent Neutrophil ADCC Assay Images
[Time]
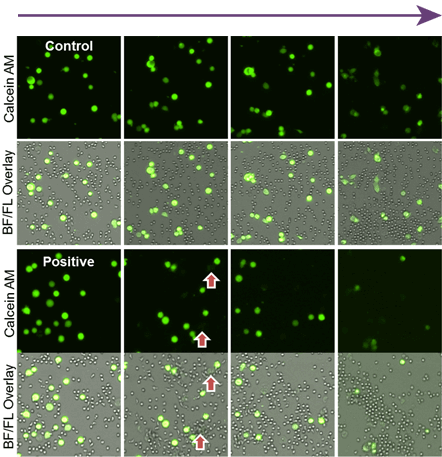
As time increased, the number of calcein AM stained target cells decreased.
In the control antibody, the neutrophil did not induce cytotoxicity.
It is clear in the bright-field/fluorescence overlay images that the neutrophils surround the target cells and induced cytotoxicity.
Neutrophil ADCC Media-Dependent Dose Response Results
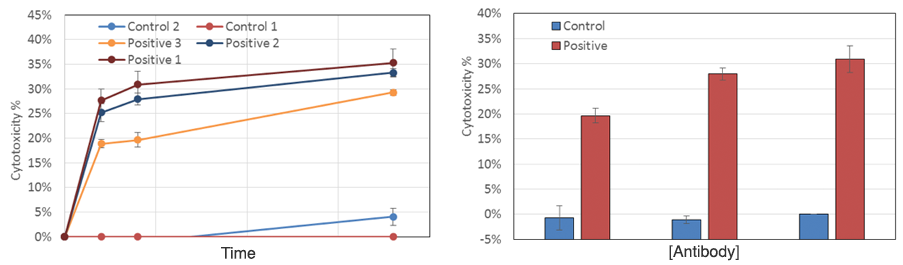
As time increased, the target cell cytotoxicity increased for the positive antibody, while the control did not show significant change. Dose-response showed positive antibody samples induced a high neutrophil-mediated ADCC effect on the target cells
Antibody-Dependent NK-Mediated Cytotoxicity using Direct Cell Counting of Calcein AM Stained Target Cells
Time
NK ADCC Time-Dependent Dose Response Results
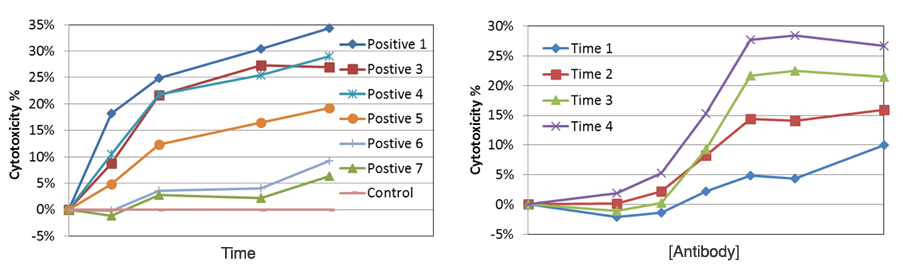
In the time-dependent graph, different antibody concentration showed a different level of cytotoxicity % over time. In the dose-dependent graph, the dose-response also showed a different level of cytotoxicity % as antibody concentration increased.
Antibody-Dependent CIK-Mediated Cytotoxicity using Direct Cell Counting of Calcein AM Stained Target Cells
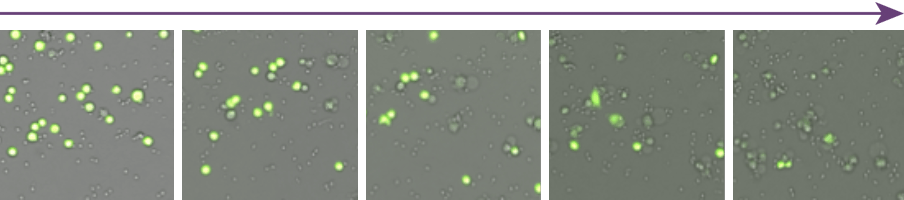
Antibody Concentration
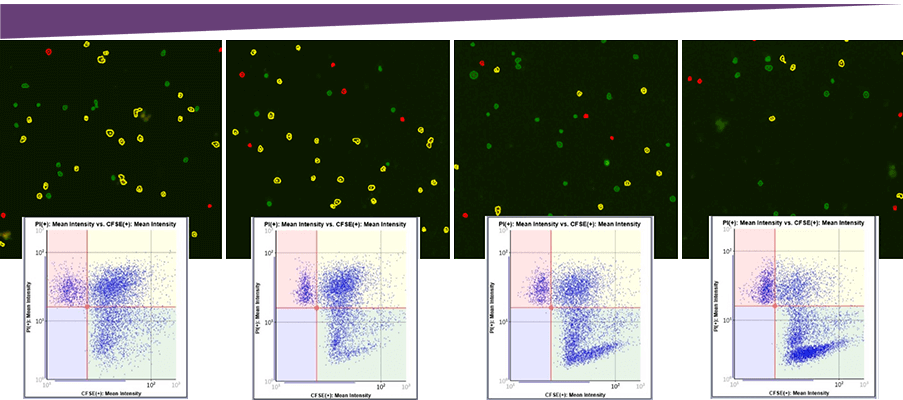
Visually, the number of dead target cells (Yellow), decreased as the antibody concentration decreased.
CIK ADCC Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity Results
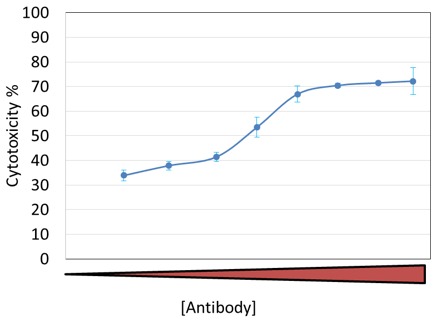
At the endpoint, a clear cytotoxicity dose response is shown with respect to antibody concentration.
The cytotoxicity % is calculated by the equation below.
As the antibody concentration increased, the cytotoxicity % also increased.
