Suspension Cell Counting
Whole-Well Imaging for Accurate Counting of Non-Uniform Cell Populations
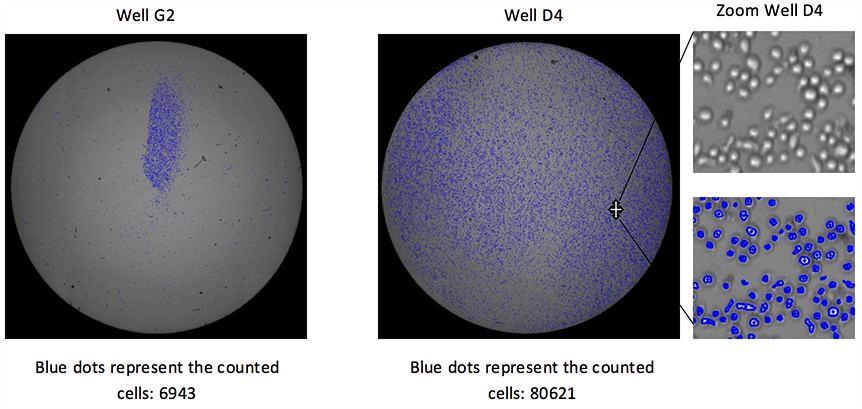
Monitor Cell Growth and Perform Live Cell Analysis of Proliferation using Label-Free Bright Field Imaging
Bright field images showing cell proliferation
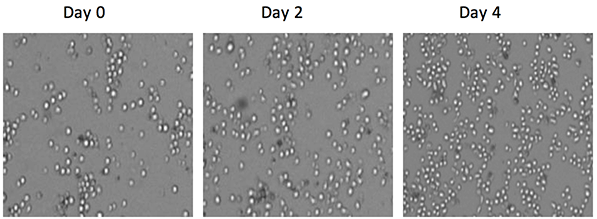
During a proliferation assay, the number of cells increased from 49323 cells on day 0 to 80621 cells on day 3 (curve on right)
Monitor cell proliferation over time
Live Cell Analysis of Total and PI-Positive Suspension Cells at an Increasing Drug Concentration
| Well | D2 | D4 | D8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BF | 87925 | 57718 | 39107 |
| PI(+) | 2654 | 7520 | 13171 |
| Viability | 96% | 87% | 66% |
The number of PI-positive cells increased in a drug dose-dependent manner
Well D2
Well D4
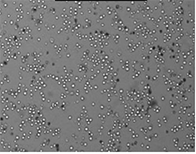
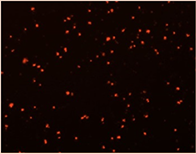
Well D8
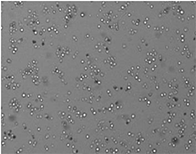
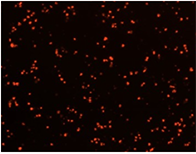

96-Well Based Cell Counting Assay for Microscale Screening Platform for CHO Cells
Assay protocol
- Use optical quality 96-well plate
- Make master dye containing Hoechst 33342 and propidium iodide
- Load 200 µl of master dye mix per well
- Add 3 µl of CHO cell suspension per well
- Incubate 40 min at room temperature
- Image 96-well plate on Celigo image cytometer (blue and red fluorescence channels)
- Use “Direct Cell Counting” image analysis parameters for Hoechst+ and PI+ cells
- Count all cells in each well
- Obtain live cell density using live cell count: Hoechst+ – PI+
- Obtain viability: (Hoechst+ – PI+)/Hoechst+
Direct Cell Counting using Image Analysis for Hoechst+ and PI+ Cells
CHO cell images
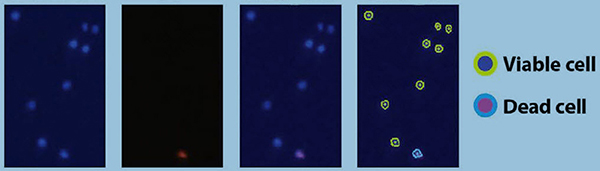
CHO cell images in the blue channel, red channel, merged image and counted cell image.
Experiment 1:
Prepared a dilution series of exponentially growing healthy CHO-S cells and examined viable cell density (VCD), coefficient of variation (CV) of VCD of healthy CHO-S cells
Comparison of viable cell density using a 96-well based Celigo method to one-sample based cell counting method.
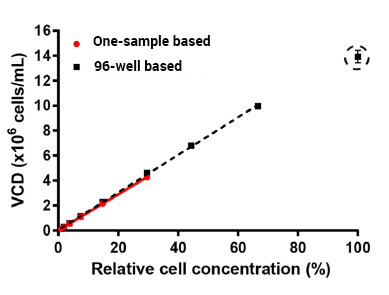
Viable cell density is plotted against relative cell concentrations for the 96-well based and one-sample based method. The dashed black line from linear regression of 96-well based method (R2 = 0.999)
Experiment 1:
Prepared a dilution series of exponentially growing healthy CHO-S cells and examined viable cell density (VCD), coefficient of variation (CV) of VCD of healthy CHO-S cells
Comparison of CV of VCD using a 96-well based Celigo method to one-sample based cell counting method.
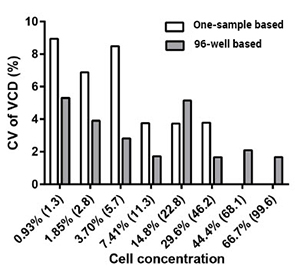
The coefficient of variation of VCD measurements is plotted against the measured cell concentration using a 96-well based and one-sample based method.
Experiment 1:
Prepared a dilution series of exponentially growing healthy CHO-S cells and examined viable cell density (VCD), coefficient of variation (CV) of VCD of healthy CHO-S cells
Viability of does not change due to cell concentration in 96-well based and single sample based samples
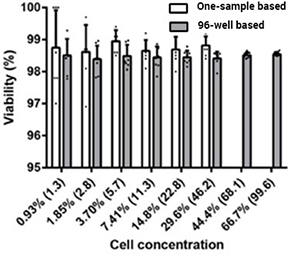
Percent viability is plotted against the measured cell concentration using the Celigo 96-well based and one-sample based method.
Experiment 2:
Cells at two concentrations were treated with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducer tunicamycin to produce a sample with lower viabilities
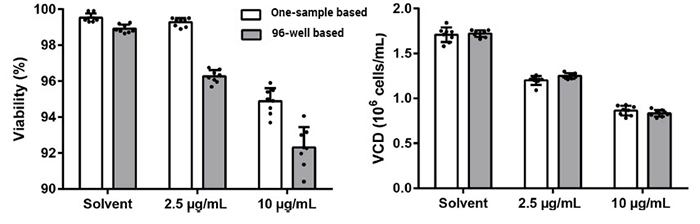
The viability and VCD decreased in a dose-dependent manner for both 96-well based and one-sample based method.
Conclusion
96-well based method versus the one-sample based method showed excellent correlation in VCD, CV of VCD, and viability measurement. Based on the performed cell dilution series, 96-well based method has a counting range from 1×105 to 1×107 live cells/mL.
