Caspase-8
Caspase-8 belongs to a family of evolutionally conserved cysteine proteases that play a key role in regulating programmed cell death or apoptosis. The two main apoptosis activation pathways are the extrinsic and the intrinsic pathways. The extrinsic pathway is activated by the binding of ligands (including TNFα, FasL, and TRAIL) to cell-surface receptors and the conversion of procaspase-8 to the active caspase-8 protease.1 Caspase-8 quickly converts procaspase-3 to active Caspase-3, facilitating many of the cellular and biochemical events of apoptosis. The intrinsic, or mitochondrial, pathway is typically activated in response to DNA or cellular damage and begins with the release of inter-membrane mitochondrial proteins.3,4 Some cancer therapies in development include molecules that trigger activation of Caspase-8-mediated apoptosis, specifically in cancer cells. Other therapies involve compounds that disrupt cancer-specific mechanisms for inhibiting Caspase-8-mediated apoptosis.5,6
Because Caspase-8 activation is such an early step in the extrinsic apoptosis pathway, measurement of Caspase-8 is an interesting alternative to measurement of apoptosis via Annexin V-FITC / PI, which involves binding to phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surface of apoptotic cells. The translocation of PS to the surface of the cell membrane occurs downstream in the apoptotic process and identifies cells committed to death through either the extrinsic or intrinsic apoptosis pathways following activation of Caspase-32.
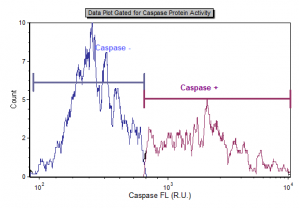
Cellometer Caspase-8 Apoptosis Kit
The CaspGLOW™Fluorescein Active Caspase-8 Staining Kit offers a simple, sensitive method for detection of active Caspase-8 in living cells. When detecting caspase-8, we utilize a specific FITC-conjugated caspase-8 inhibitor, IETD-FMK. IETD-FMK is cell-permeable and binds irreversibly to active caspase-8 within the cell. The fluorescent marker (FITC) on the IETD-FMK allows for the detection of cells undergoing apoptosis via Caspase-8 activation using the Vision CBA Analysis System. Caspase-8 activity is presented as a population percentage and caspase-positive cell concentration.
Caspase-8 References:
1) Hengartner, M.O. (2000). The Biochemistry of Apoptosis. Nature, 407(6805), 770-776.
2) Taylor RC, et al. (2008). Apoptosis: Controlled Demolition at the Cellular Level. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 9 (3): 231-241.
3) Fulda, S., et al. (2006). Extrinsic Versus Instrinsic Apoptosis Pathways in Anticancer Chemotherapy. Oncogene, 25, 4798-4811.
4) Spencer. S.L., et al. (2011). Measuring and Modeling Apoptosis in Single Cells. Cell. 144, 926-939.
5) Naoghare, P.K., et al. (2009). Simultaneous Quantitative Monitoring of Drug-induced Caspase Cascade Pathways in Carcinoma Cells. Integrative Biology. 2, 46-57.
6) Fulda, Simone (2011). Targeting Apoptosis Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 3, 241-251.


Leave A Comment