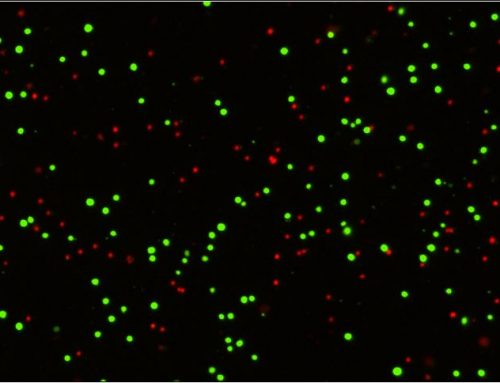
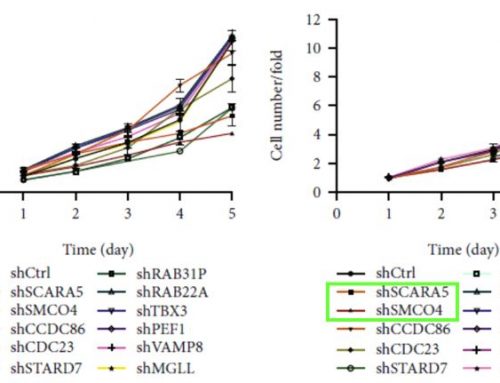
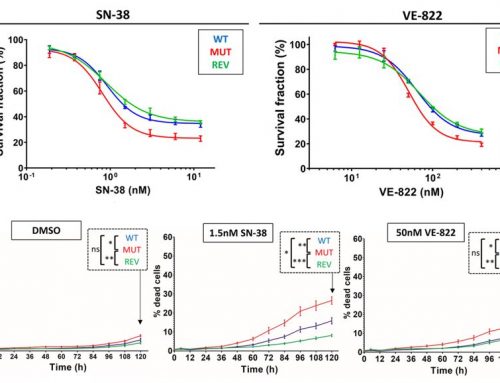
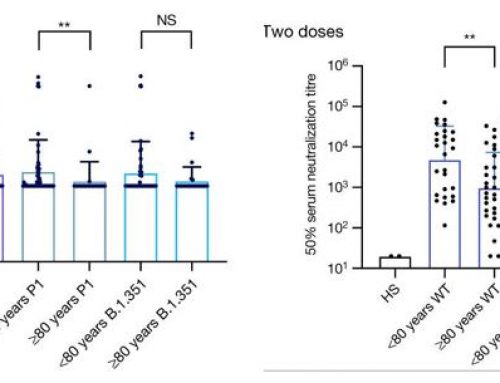
The Notch-disrupting and cancer stem cell-inhibiting effects of the drug quinomycin A were investigated at the University of Kansas Medical Center. Using human pancreatic cancer cells PanC-1, MiaPaCa-2, and BxPC-3 and the Celigo to determine the number and size of pancreatospheres, researchers evaluated the drug’s ability to block cancer stem cell growth via inhibition of the Notch signaling pathway. After administration of the drug, proliferation and colony formation were blocked in cancer cell lines but not in normal pancreatic epithelial cells. Furthermore, cancer stem cell markers were reduced as was pancreatosphere formation. This work identifies quinomycin A as an efficacious inhibitor of pancreatic cancer stem cells.
Read the full publication here.
The Celigo image cytometer can be used in a wide array of applications and experiments. Visit our website to learn more about how the Celigo could benefit your research.

Leave A Comment