Obtain fast, accurate and consistent cell viability and concentration measurements of primary murine samples in <30 seconds using the Cellometer K2!
The use of mouse models is common across multiple fields of study and the samples acquired greatly vary in type and complexity, from splenocytes to tissue digests to tail vein blood.
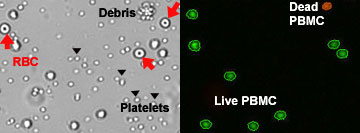
- Tissue debris, cell debris, and red-blood cell contamination can lead to inconsistent cell counts from sample to sample when performing manual counting.
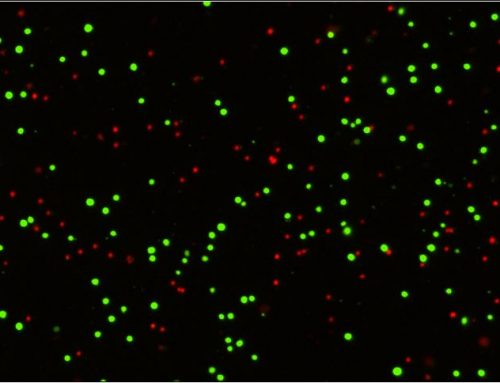
- Nexcelom’s Cellometer instruments perform fluorescent based analysis using nucleic acid dyes Acridine Orange/ Propidium Iodide (AO/PI).
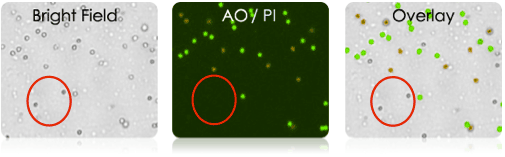
- In the dual color, AO/PI viability assay, only nucleated cells are stained and counted. Non-nucleated cells and cellular debris are not stained and therefore are not counted.
Download Our PBMC White Paper
Accurately Count PBMC and Measure Viability in Presence of Residual RBC
Learn More:
Accurately Count Mouse Primary Samples in the Presence of Cell Debris »
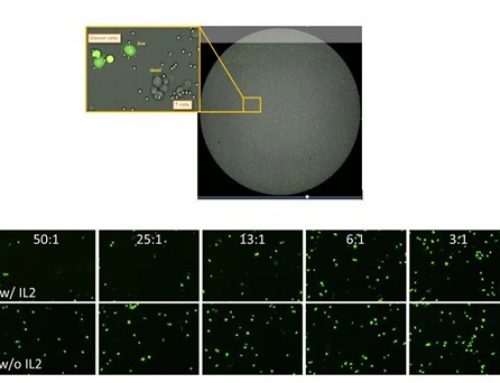
Only nucleated cells are detected in each sample
Viability and Concentration are automatically reported after cell counting is completed.
Measurements are based on the fluorescent detection of live (green) and dead (red) cells only.
Non-nucleated cells (shown in the red circle) are not stained and are not counted.
Learn More:
Accurately Count PBMC and Measure Viability in Presence of Residual RBC »
Because platelets and mature red blood cells do not have a nucleus, they are not stained by nuclear staining dyes.
With the dual-fluorescence method, there is NO counting error from RBCs, platelets, or debris. Lysis of RBCs is not necessary.

Leave A Comment