Morphology
Identify, Characterize and Monitor Cell Populations Based on Morphology
A mixture of adherent and suspension cells were seeded into a 96-well plate. Using the Celigo gating interface, we provide a live cell analysis method to can identify two distinct populations using morphology. Designed to produce the enhanced bright field cell image, in combination with the advanced image analysis software, Celigo has been used to identify, characterize and monitor specific cell sub-populations based on morphological features.
Population analysis based on cell roundness
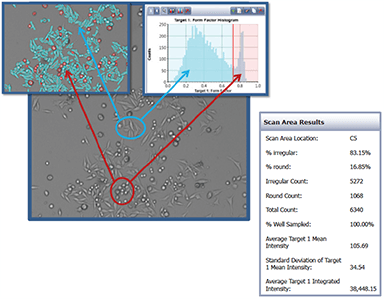
A mixture of adherent and suspension cells were seeded into a 96-well plate. Using the Celigo gating interface we can identify two distinct populations using morphology only. Designed to produce the enhanced bright field cell image, in combination with the advance image analysis software, Celigo has been used to identify, characterize and monitor specific cell sub-populations based on morphological features. Celigo imaging cytometer records cell images, displays gated cell images, calculates cell morphological parameters and plots the data for population gating.
Camptothecin-induced morphological changes
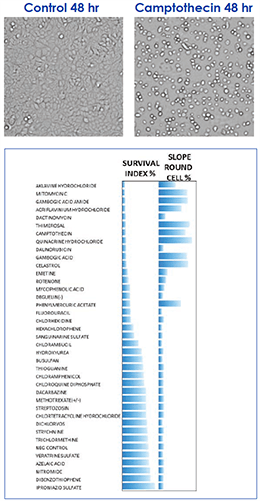
Alteration in cellular morphology was used as an indicator of compound toxicity. We can observe an example (far left) of the rounding up of an adherent cell after 48 hrs treatment with Camptothecin. Using this alteration in morphology in a label-free assay, we screened a number of compounds. The % survival index calculated from this assay is shown (left).
Bright Field Images of Colo-205 Cells on Celigo Cell Imaging Cytometer
Monitor drug-induced morphological changes
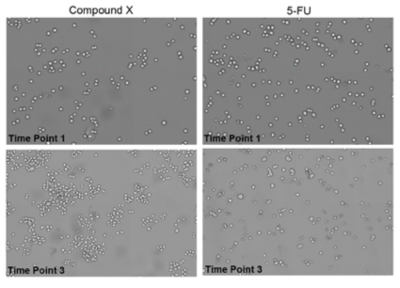
Cells were treated with Compound X (left) and 5-FU (right) and images were acquired at multiple time points. After 5-FU treatment, a morphological change is observed at time point 3.
