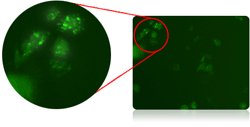
Cellometer Vision Image Cytometer was used to capture and identify fluorescent positive GFP-LC3 cells.
Autophagy is an important cellular catabolic process that plays a variety of important roles, including maintenance of the amino acid pool during starvation, recycling of damaged proteins and organelles, and clearance of intracellular microbes. First, the damaged proteins, organelles or foreign microbes are isolated by double membrane vesicles called autophagosomes. The vesicles then complete the enclosure of the damaged organelles and then fuses with lysosome. to form autolysosomes. Finally, the materials are degraded within the autolysosomes and the nutrients are recycled back to the cell. Currently employed autophagy detection methods include fluorescence microscopy, biochemical measurement, SDS-PAGE, and Western blotting, but they are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and require much experience for accurate interpretation.
By utilizing image cytometry, fluorescently labeled autophagosomes can be detected and measured via fluorescence analysis. Cellometer Vision has been used to demonstrate the detection and measurement of total fluorescence intensity of fluorescently labeled autophagosomes using proprietary stains (Cyto-ID® Green dye from Enzo Life Sciences) and GFP-LC3 protein in live cells.
The image cytometry method has been shown to generate comparable fluorescence intensity data to flow cytometry, which can be an alternative method to indicate the autophagy activity level in live cells. This can serve as a useful method to quickly assess autophagic response of live cells when treated with various chemical or biological reagents, as well as an alternative technique available in support of autophagy-based drug discovery relating to various pathological disorders.


Leave A Comment