Bone marrow, cord blood, whole blood, and peripheral blood are routinely processed in many different laboratories. Whether for cryopreservation or for downstream isolation of specific nucleated cells, (such as stem cells, B-cells, or T-cells) accurately measuring cell concentration and viability is paramount to the overall success of the project.
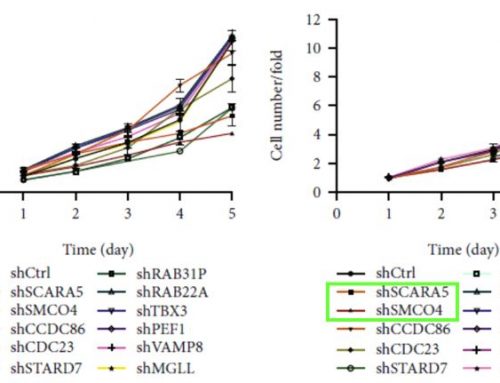
- Many blood-based samples (whole blood, peripheral blood, bone marrow, PBMC, cord blood, etc…) may contain residual red blood cells even after RBC lysis. (See figure below)
- When samples are enumerated using manual counting, the presence of residual RBCs can lead to inaccurate cell concentration and viability readings.
- Nucleic acid dyes, acridine orange (AO) and propidium iodide (PI), only stains nucleated cells and therefore yields accurate and consistent results.
- The Cellometer image cytometers acquire multiple images and automatically reports the concentration of nucleated cells and percent viability.
Download the Application Note: Viability for Blood-based Samples
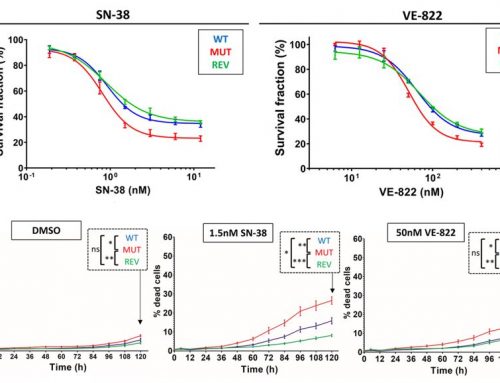
- Live, AO positive, white blood cells (WBCs) are green
- Dead, PI positive, WBC are red
- In this PBMC sample, red circles indicate contaminating RBCs that are seen in the bright-field image but are not stained with AO/PI.
- The Cellometer accurately and automatically reports the cell concentration and viability in less than 30 seconds!
Learn more about Cell Concentration and Viability of Clinical Samples »



Leave A Comment